

This repository provides all the tools and step-by-step guide needed to convert a high-fidelity audio source into a high-quality digital audio stream, making your vinyl record collection or other analog audio sources accessible across a wide range of digital platforms using Icecast.
At the heart of this setup is the Raspberry Pi, a small and affordable ARM-based computer that serves as the audio streaming server (commonly referred to as music streamer or network streamers when sold as a prebuilt applicance).
Other than your audio source you are also going to need an external audio capture device that provides line-in interface ports and ADC (analog-to-digital converter) + an external preamplifier if your turntable does not have built-in preamp (or if want to disable the built-in preamp).
An alternative to using an external audio capture device is to buy an audio source with embedded USB audio codec output, like a “USB turntable” (there are several different models of “USB turntables” of various quality on the market but many might not be suitable for audiophiles).
Disclaimer: I have personally tested this solution using the combination of a Behringer UCA202 USB Audio Device for analogue-to-digital conversion and capturing + a PHONO PP400 preamplifier, but in theory this method should work with every other Raspberry-compatible capture device and with any other preamplifier.
-
Preamplication: Your turntable’s audio output is first routed through a preamplifier (also known as a phono preamp), that converts a weak signal into an output signal strong enough to be noise-tolerant and strong enough for further processing. Without this preamplication, the final signal would be noisy or distorted. The preamp also ensures that your records sound balanced and accurate.
-
Analog Audio Capture and Digital Conversion: The amplified signal from the pre-amp is fed into the audio capture device, where it is digitized using its ADC (analogue-to-digital converter) and sent to the Raspberry Pi.
-
Streaming: On the Raspberry Pi, two critical software components that come into play:
- Darkice: This live audio streamer that captures/records the digital audio from the audio interface and encodes it into a streamable audio format.
- Icecast: This “internet radio” streaming media server takes the encoded audio from Darkice and broadcasts it, making it accessible to listeners locally via HTTP URL or over the internet.
-
Quick Start: For those eager to get started, a pre-configured Raspberry Pi image is available for download. Simply flash it onto a Micro SD card, insert the card into your Raspberry Pi, and you’re ready to stream.
-
Manual Configuration: For users who prefer to fine-tune their setup, step-by-step instructions are provided for configuring Darkice and Icecast, as well as identifying and setting up your audio capture device.
After that, you will have a stream on your local network which you can access with multiple programs such as iTunes, VLC Player, or Chrome. From these programs, you can also stream your audio to multiple rooms using Google Chrome or AirPlay 2.
To facilitate capturing and digitizing audio from an analog source and streaming it you are going to have to need a few things.
Ensure that you have all the prerequisite hardware components mentioned below before proceeding with the setup.
If you own an Hi-Fi audio source equipment like an LP record player/turntable that only has analog audio output (.i.e. it does not have an embedded USB audio codec output) then the easiest option is to buy and use an external stand-alone USB Audio Device for analogue-to-digital conversion. These mentioned solutions most often support utilizing a USB Audio Class 2.0 pipeline that can support high-definition audio formats up to 192KHz and 32bits using a standard digital audio interface, however, you need to check the specification before buying the device to make sure it meets your own reqirements.
Examples of known compatible Audio Capture Device hardware equipment:
- Behringer UCA222 (without pre-amp, newer model that is a direct replacement for the UCA202)
- Behringer UCA202 (without pre-amp)
- Behringer UFO202 (with pre-amp)
- ART USB Phono Plus (a standalone pre-amp with USB interface that needs external power-suppy).
- IK Multimedia iRig Stream (without pre-amp)
- IK Multimedia iRig Stream Pro (with pre-amp)
Another option as ADC instead of a USB Audio Device that should technically provide the same function but has not been tested here are HiFiBerry’s ANALOG INPUT products like “HiFiBerry DAC+ ADC PRO”, “HiFiBerry DAC2 ADC PRO”, or “HiFiBerry DAC+ ADC” as input, (which as bonus using HiFiBerry makes the whole build an all-in-one package that could be aesthetically pleasing and almost have the clean look of a commercial appliance):
- https://www.hifiberry.com/blog/need-some-input/
- Official HiFiBerry cases for Raspberry Pi: https://www.hifiberry.com/shop/#cases
Note that not all HiFiBerry boards have been tested as with the Raspberry Pi 5 (so double-check board compatible if that is what you decide to go with):
- https://www.hifiberry.com/blog/pi5-compatibility-with-hifiberry-products/
Note that some but not all vinyl record players (turntables/phonographs/gramophones) have a built-in preamplifier (also known as a “phono preamp”, “phone stage”, or “RIAA pre-amp”), and even if they do you still often have the option to disable the built-in preamplifier in favor of using an external preamp of higher quality or a other RIAA EQ curve for a different sound.
If your Hi-Fi audio source equipment does not have a built-in pre-amp for analog output then you either need to buy specifically a USB Audio Device with pre-amp (like one of ones mentioned above) or use a separate high-fidelity preamplifier (RIAA/phono preamp) to put inline between the audio source equipment and the Audio Capture Device, (this preamp stage amplify the very quiet electrical signal generated by the cartridge on your vinyl turntable, as otherwise you will not get a high-quality signal that has been amplified enough to allow good digitalization).
Examples of known good preamplifier hardware equipment:
- PHONO PP400
Tip: If you are into electronics DIY then you can build your own following build instructions from the “Calvin-phono”, “PlatINA”, or RP1 projects:
Note! Regardless of which preamp you end up using, recommend get and use a galvanicly isolated power-supply or in-line galvanic isolator made for audio in-mind as that prevent ground loop noises and increase sound quality, (works by creating a new ground for the USB device).
- “Raspberry Pi 3 Model B” or a “Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W”
- Micro SD Card – (8GB is enough for a dedictaed solution).
- A good quality USB power-supply, (audio applications/equipment can be much more sensitive to power supplies).
- Optionally: Get an “USB isolator” or a USB power-supply with built-in isolator.
- Again, as mentioned above under the preamplifier section, galvanicly isolated power-supply or galvanic isolator is recommended for all components to prevent ground loop noises and increase sound quality.
- Optionally: Get an “USB isolator” or a USB power-supply with built-in isolator.
Download the Raspberry Pi Imager from Raspberry Pi Software.
Also, download the preconfigured image for your project from GitHub: Download Image.
- Insert your Micro SD card into your computer.
- Open the Raspberry Pi Imager.
-
Choose OS: Select “Custom Image” in the dropdown menu. Select the Downloaded preconfigured image.
-
Choose Storage: Select your SD card as the storage destination.
-
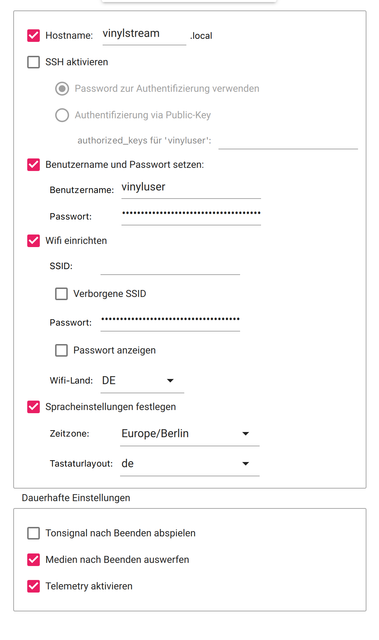
Settings: Click on the Settings tab and input the following information:
- Hostname:
vinylstream - User:
vinyluser# Important: The username must be exactly the same. Also pay attention to uppercase and lowercase letters - Password:
setyourpassword# Is no longer needed after the easy installation - Input your Wi-Fi information.
- Hostname:
-
Save these settings.
-
Click on “Write” and wait for the process to complete.
- Insert the Micro SD card into your Raspberry Pi.
- Connect the Raspberry Pi to a power source.
- Connect the capture card to the Pi.
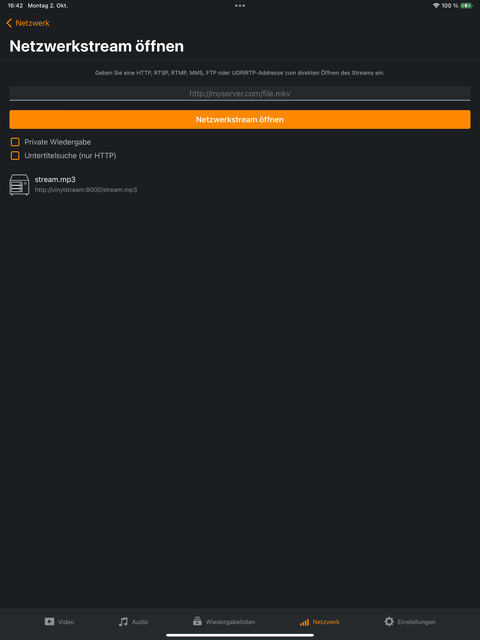
Wait for 3-5 minutes, then try to open this page in your browser: http://vinylstream:8000/
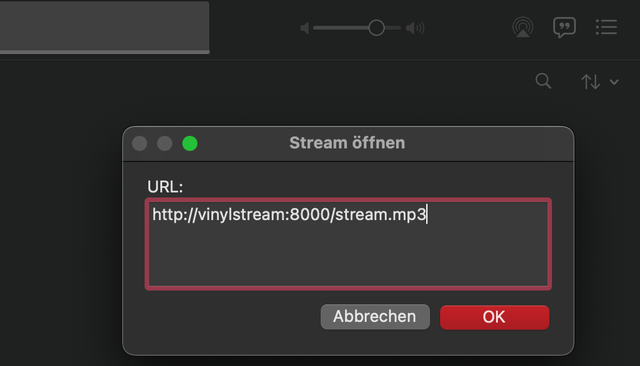
That’s it! You can now stream your music from http://vinylstream:8000/stream.mp3.
Press inside the iTunes (Music) App: ⌘U (Command U)
Then type in http://vinylstream:8000/stream.mp3
# Lists audio devices
arecord -lLook for the output that identifies your Behringer UCA202. For example:
**** List of CAPTURE Hardware Devices ****
card 1: CODEC [USB Audio CODEC], device 0: USB Audio [USB Audio]
Note down the card and device numbers as you will need them for configuration (e.g., hw:1,0).
# Captures 10 seconds of audio and saves it as test.wav
arecord -D hw:1,0 -d 10 test.wavThe command will record 10 seconds of audio from your capture device. Play the test.wav file to check the audio quality. If everything sounds good, proceed with configuring Icecast.
To manually set the sample rate, you can use:
# Sets the sample rate and captures 10 seconds of audio
arecord -D hw:1,0 -d 10 -f S16_LE -r 48000 test.wavFor the Behringer UCA202 for example, the max sample rate is 48 kHz
Before we dive into the configuration part, it’s crucial to install and understand the role of two essential software components for this setup: Darkice and Icecast.
Darkice is a live audio streamer that captures audio from your specified device (in this case, Behringer UCA202) and encodes it into a streamable format. It acts as the bridge between your audio capture device and the Icecast server, capturing audio in real-time and sending it to Icecast for distribution.
Icecast is a streaming media server that will broadcast the audio stream to listeners. It’s highly configurable and handles multiple clients, allowing you to stream audio to numerous listeners simultaneously. Icecast takes the encoded audio feed from Darkice and makes it accessible over the internet.
If you haven’t installed these yet, you can do so with the following commands:
For Darkice:
sudo apt-get install darkiceFor Icecast:
sudo apt-get install icecast2-
Open the Darkice configuration file, usually named
darkice.cfg, in a text editor.sudo nano /etc/darkice.cfg
-
Insert the configuration code provided in the referenced Git repository. This code typically sets the input device, sample rate, and other parameters tailored for optimum performance with your Behringer UCA202 capture device.
Note: The Git repository is your go-to source for a sample configuration. Simply copy-paste the code into your
darkice.cfgfile.
If you dont want to set Darkice as a system service, you can manually start it using the custom configuration file:
# Starts Darkice with the custom configuration file
darkice -c /path/to/darkice.cfgIn this case, you will need to run this command each time you wish to start Darkice. Make sure to replace /path/to/darkice.cfg with the actual path to your Darkice configuration file.
Either method will initiate Darkice, allowing it to capture audio based on the parameters set in your configuration file and send it to the Icecast server for streaming.
If you find yourself frequently using Darkice and Icecast, setting them up as system services can automate the startup process and help manage the applications more efficiently.
To set up Darkice as a system service, you can create a custom systemd service file:
-
Create a new systemd service file for Darkice.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/darkice.service
-
Add the following content:
[Unit] Description=Darkice live audio streamer After=default.target [Service] ExecStartPre=/bin/sleep 10 ExecStart=/usr/bin/darkice -c /etc/darkice.cfg Restart=always User=vinyluser [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Note: Replace
/etc/darkice.cfgwith the actual path to your Darkice configuration file andvinyluserwith the user you want the service to run as. -
Reload the systemd daemon and enable the service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable darkice
sudo systemctl start icecast2
sudo systemctl enable icecast2 # start on boot
Icecast usually installs itself as a service by default. If for some reason it isn’t, you can create a custom systemd service file similar to Darkice.
- Connect to your stream using a web browser (Chrome) or a streaming app (iTunes / VLC).
- Listen to some music
If all goes well, your quality audio streaming setup is now complete!
- https://github.com/gieljnssns/darkice-libaacplus-rpi-guide
- https://maker.pro/raspberry-pi/projects/how-to-build-an-internet-radio-station-with-raspberry-pi-darkice-and-icecast
- https://github.com/aschober/vinyl-cast
- https://www.instructables.com/Stream-AUX-and-Bluetooth-Through-Raspberry-Pi-to-W/
- https://dupontgu.medium.com/how-to-stream-your-record-player-throughout-your-home-for-cheap-fb044368a240
- https://www.instructables.com/Add-Aux-to-Sonos-Using-Raspberry-Pi/
 https://github.com/quebulm/Raspberry-Pi-Vinyl-Streamer
https://github.com/quebulm/Raspberry-Pi-Vinyl-Streamer